The Beginning of America: From Colonies to American Revolution
The history of the United States is a story of resilience, determination, and innovation. It officially began in 1492, when the famous explorer Christopher Columbus set foot on the shores of the New World. This discovery marked the start of European colonization, with major colonial powers such as Britain, France, and Spain racing to establish control over the rich and fertile lands of the newly discovered continent.
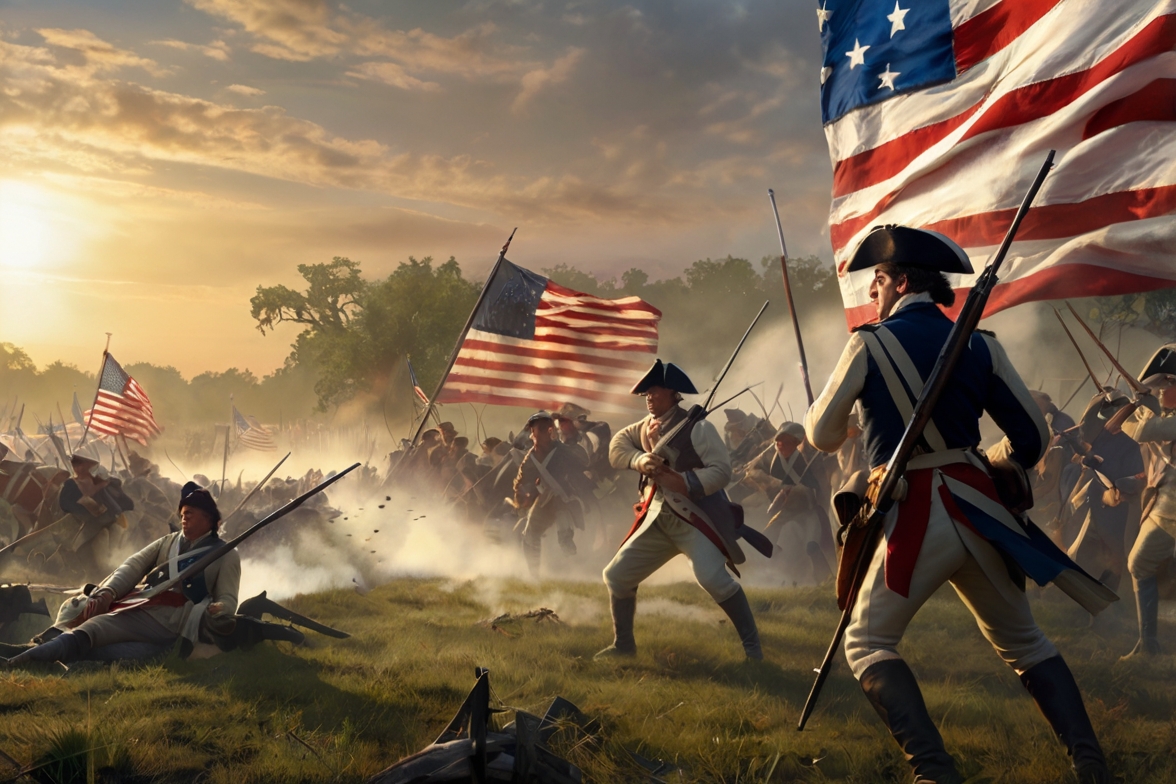

Spain dominated the southern and western regions, while France expanded its influence along the Mississippi River. However, it was Britain that secured the eastern seaboard and established 13 colonies, which would eventually form the foundation of the United States. These colonies thrived on trade, agriculture, and maritime commerce, but tension grew steadily due to the oppressive policies imposed by the British government.
Table of Contents
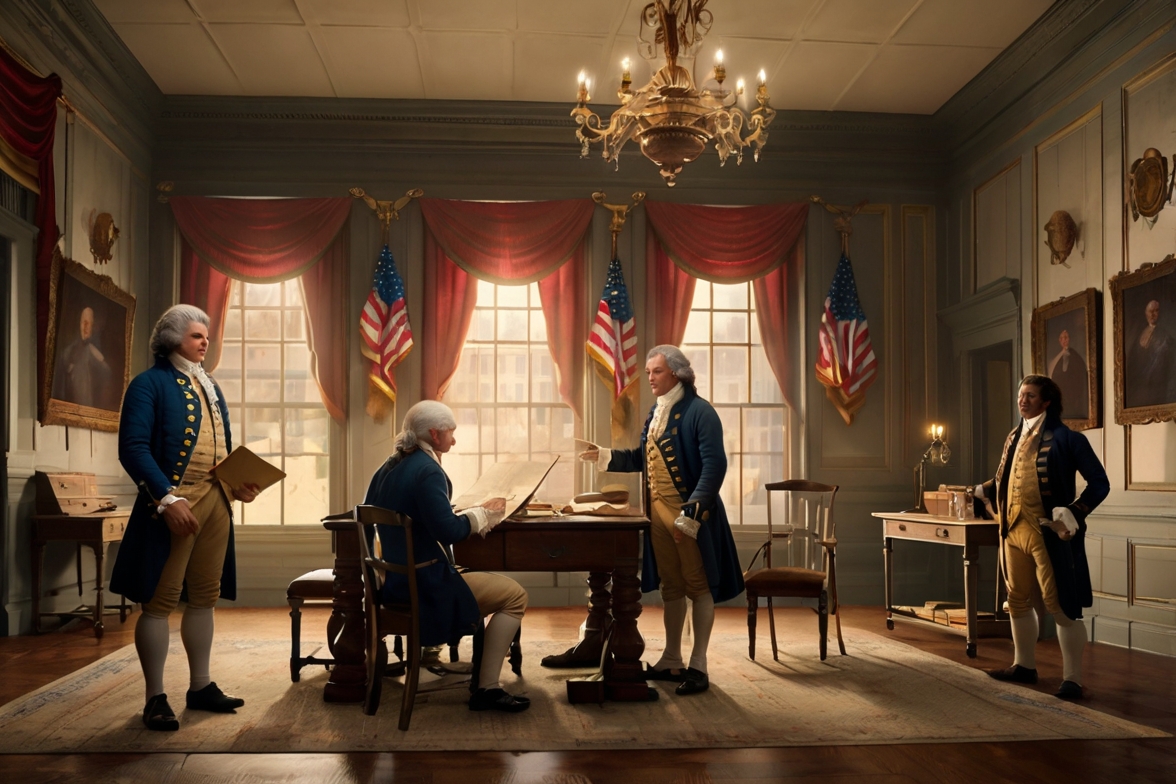

The Road to Rebellion: The Boston Tea Party
The situation reached a boiling point in 1773 with the infamous Boston Tea Party. Colonists, frustrated by the heavy taxation and lack of political representation, protested by throwing a shipment of British tea into Boston Harbor. This event became a symbol of resistance against British rule and a catalyst for the American Revolution.
The Declaration of Independence (1776)
On July 4, 1776, under the leadership of Thomas Jefferson, the Declaration of Independence was signed, marking a turning point in world history. This powerful document proclaimed the 13 colonies’ separation from British rule and established their intent to form an independent nation. Prominent leaders such as George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, and John Adams played a crucial role in this movement, inspiring the American people to fight for their freedom.
The American Revolution (1775–1783)
The American Revolution was a challenging and prolonged conflict that lasted from 1775 to 1783. Despite the formidable strength of the British military, the American forces, with the support of local militias and foreign allies like France, achieved a historic victory.
The decisive moment came in 1781 with the Battle of Yorktown, where British General Lord Cornwallis surrendered to American and French forces, effectively ending the war. The Treaty of Paris (1783) officially recognized the United States as an independent nation, paving the way for the creation of a new democratic state.
The Birth of American Democracy
Following independence, the newly formed nation faced the challenge of building a government that reflected the principles of liberty and equality. The U.S. Constitution, drafted in 1787, laid the foundation for a strong democratic system that endures to this day. George Washington, the esteemed military commander, was unanimously elected as the first President of the United States in 1789, setting the standard for future leaders.
The Expansion and Development of the Nation
With independence secured, the United States began expanding westward, acquiring new territories and integrating them into the growing nation. This era of expansion brought tremendous opportunities, but also significant challenges, including conflicts with Native American tribes and debates over the future of slavery. Despite these difficulties, the nation’s infrastructure grew, its population expanded, and its economy flourished.
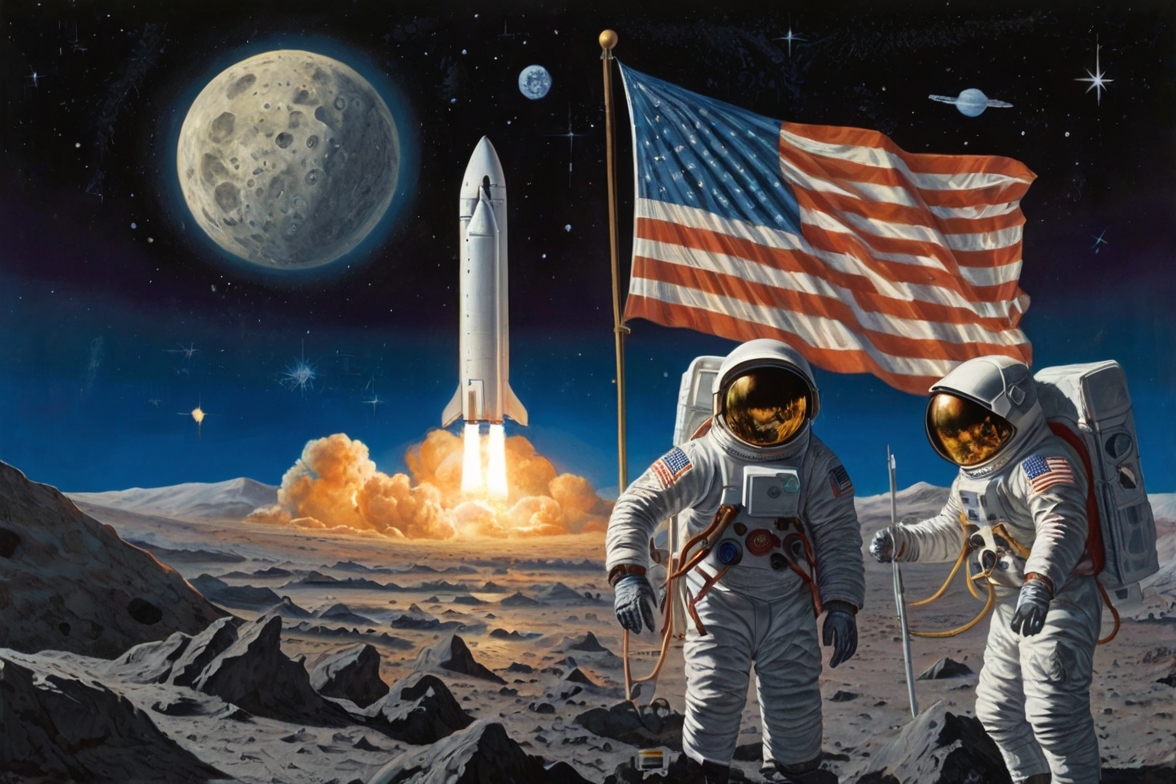

America’s Space Missions and Scientific Achievements
In addition to its remarkable historical journey, America has always been at the forefront of scientific innovation and exploration. The country’s space program, led by NASA, has achieved some of the most groundbreaking milestones in human history.
The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 was a defining moment when Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on the moon, famously declaring, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” This success positioned the United States as a global leader in space exploration.
Subsequent missions have continued to push the boundaries of human knowledge. From the Mars Rover missions to the development of the International Space Station (ISS), American scientists and engineers have been instrumental in expanding our understanding of the universe. These achievements reflect the nation’s enduring commitment to progress and exploration.
Scientific Innovations and Technological Advancements
America’s history is rich with scientific discoveries and technological advancements that have transformed the world. Innovations such as electricity, the telephone, the internet, and modern medicine owe much to American inventors and researchers. The country’s emphasis on research and development has created a thriving ecosystem for scientific breakthroughs, making it a global hub for innovation.
The Modern Education System in America
Another cornerstone of America’s success is its modern education system, which is recognized globally for its quality and diversity. The United States is home to some of the world’s top universities, such as Harvard, MIT, and Stanford, which attract students and scholars from around the globe.
The American education system emphasizes critical thinking, creativity, and innovation, preparing students for leadership roles in various fields. Public and private institutions, along with numerous research centers, contribute to the country’s academic excellence, ensuring that future generations remain equipped to meet the challenges of a rapidly evolving world.
Conclusion
The story of America is a testament to human resilience, ambition, and the desire for progress. From its humble beginnings as a group of colonies to its current status as a global superpower, the United States continues to inspire the world with its achievements in history, science, and education. Its journey is far from over, and as it continues to evolve, America remains a symbol of opportunity, innovation, and freedom for millions around the globe.
FAQs: The History, Development, and Achievements of the United States
1. When did America gain independence?
America declared its independence on July 4, 1776, through the Declaration of Independence. However, independence was officially recognized in 1783 after the signing of the Treaty of Paris.
2. What was the American Revolution?
The American Revolution (1775–1783) was a conflict between the 13 American colonies and Great Britain. It resulted in the colonies gaining their independence and forming the United States of America.
3. What is the U.S. Constitution?
The U.S. Constitution, drafted in 1787, is the supreme law of the United States. It established the framework for the federal government and guarantees fundamental rights to its citizens.
4. What are some key scientific achievements of the United States?
The United States has made numerous scientific breakthroughs, such as the invention of the telephone, the light bulb, the airplane, and the internet. In space exploration, the U.S. was the first to send astronauts to the moon in 1969 through the Apollo 11 mission.
5. What is NASA, and why is it important?
NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) is America’s space agency responsible for space exploration and scientific research. It has led historic missions, including the Apollo moon landings, Mars Rover missions, and the development of the International Space Station (ISS).
6. Why is America’s education system considered advanced?
America’s education system is renowned for its world-class universities, cutting-edge research, and emphasis on critical thinking and innovation. Institutions such as Harvard, MIT, and Stanford consistently rank among the top in the world.
7. How did America become a global superpower?
America’s rise to global prominence is attributed to its economic growth, scientific advancements, military strength, and its leadership in innovation and education. Its role in World War II, followed by its achievements in space and technology, further solidified its superpower status.
8. What are some important milestones in American space exploration?
- 1961: First American astronaut, Alan Shepard, went to space.
- 1969: Neil Armstrong became the first human to walk on the moon during Apollo 11.
- 1973: The U.S. launched its first space station, Skylab.
- Present: Ongoing Mars Rover missions and plans for a human mission to Mars in the near future.
9. What role did George Washington play in American history?
George Washington was the commander of the Continental Army during the American Revolution and later became the first President of the United States (1789–1797). He is often referred to as the “Father of His Country.”
10. Why is the Declaration of Independence significant?
The Declaration of Independence is a landmark document that declared the American colonies free from British rule. It outlined the principles of liberty, equality, and the right to self-governance, which became the foundation of American democracy.









Post Comment